News
Horse Health
-

USDA Announces Rabies Action Plan to Protect Public, Domestic Animals and Wildlife
Rabies is a viral disease of mammals, transmitted from the bite of a rabid animal and direct contact with saliva or brain/nervous tissue from the animal and has the highest fatality rate of any known disease.
-

Five Horses Test Positive for Eastern Equine Encephalitis in New York
Although New York has seen several triple E cases in horses this year, there haven’t been any human cases, which is fortunate because, unlike for horses, there’s no human vaccine for EEE.
-

Warning for Horse Owners: Ticks Are Out During the Fall Season
Protecting equines from ticks during the fall is a topic worth investing some time and interest in since ticks hatch their eggs in leaves, leaf mulch, and dry brush.
-

Survey of the knowledge and Perceptions of Horse Owners in Ireland of Common Clinical Conditions and Their !mpact
Pain, discomfort, and quality of life were reported as the most common concerns when their horse has a medical condition or when considering euthanasia.
-

Grand Meadows Cares Series: Read Your Equine Supplement Label Two Ways to Optimize Horse Safety
The NASC seal gives the consumer some level of protection against companies that have no clue what they are doing, are simply out to make a quick buck or execute nefarious business practices.
-

Autumn Challenges for Horse Owners
While fall weather often brings pleasant conditions, it also brings conditions that are frustrating and create extra work for both horse and owner.
-

Vesicular Stomatitis in Horses in the State of California - Update
Outbreaks of vesicular stomatitis virus usually occur during the warm summer months, particularly in animals pastured along waterways.
-
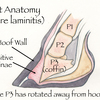
Take Your Horse’s Digital Pulse
Learn how and where to take your horse's digital pulse.
-

Senior Horse Education Month Featuring Short Online Course and Free Tool!
Keeping a horse comfortable in their senior years requires an attentive caretaker backed by a knowledgeable team.
-

Keeping Your Horse Safe on Fall Grass
Fall means that horse owners need to reconsider their grazing strategies, especially for those horses with metabolic issues.