News
Horse Health
-

Virology: Equine Hepatitis Viruses and Hepatitis C
The equine hepatitis virus infection of horses could represent a powerful model to gain insights into hepaciviral evolution and hepatitis C virus immune evasion.
-

Colic or Rabies — Similar Symptoms Can Place Horse Owners at Risk
Through rabies vaccination in horses, horse owners' exposure to rabies - which is a zoonotic disease - is prevented.
-

5 FAQs: Understanding the Equine Disease, PPID
By focusing on stress, health and comfort, horse owners can reduce the impact PPID has on their horse's life.
-

Maintaining Senior Horse Health through Proper Feeding and Care
Your veterinarian or equine nutritionist can help you determine how to best satisfy your senior’s dietary needs when weight becomes an issue.
-

Helping Your Senior Horse Stay Fit as She Ages
A horse's earlier career influences which fitness program will suit him best later in life, since it is easier to get an older athlete back in shape than it is to transform an aged equine loafer into a top performer.
-

Research on Reduced Frequency of Parasite Treatment in Horses Reveals Important Information for Horse Owners
Model simulations indicated that whole-herd treatment regimen with at least 4 macrocyclic lactone treatments led 2-3 times faster resistance development than alternative treatment regimens.
-

Learn About the Equine Herpes Virus (EHV) Outbreak in California on March 17, 2022
Presentation on EHV will be given by Dr. Robert Keene, Boehringer Ingelheim Professional Services Veterinarian, with plenty of time to answer questions!
-

Office of the State Veterinarian Has Issued Information and Warning Regarding California EHV-1 Outbreak
To reduce spread of EHV-1, it is recommended that all hunter/jumper events be postponed for the next 28 days, all equine events be postponed for 14 days, and non-essential horse movements postponed for at least 14 days.
-
Peace of Mind Comes with a Small Price When Caring for Horses
In addition to vaccinating for core diseases, your veterinarian will also evaluate your horse's risk of exposure to other diseases such as Equine Influenza, Potomac Horse Fever and Strangles.
-
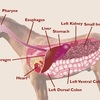
New Equine Fecal Transplant Research Reveals Challenges to Successul Microbiota Transplantation
One challenge to fecal microbiota transplantation is the path to the colon is much longer in a horse, precluding administration by enema for example, and requiring delivery into the stomach via the nose instead.